What is the Best Materials and Tools for Sustainable Building Projects?
Sustainable building projects rely heavily on the right materials tools. As sustainability expert Dr. Emily Green once said, "The choice of materials can make or break a project." This statement highlights the essential role that quality materials tools play in constructing eco-friendly buildings.
When considering sustainable practices, it's vital to think beyond conventional solutions. Many builders still resort to outdated materials. However, innovative options are emerging. Recycled materials, for example, are reshaping project guidelines. They not only reduce waste but also often prove cost-effective. Yet, some may question their durability compared to traditional choices. This skepticism can hinder progress in sustainable construction.
Moreover, the tools used in these projects are equally important. Advanced technologies and techniques can enhance the efficiency of material usage. Traditional tools may not meet the unique demands of sustainable building. Builders must embrace these changes to ensure long-term benefits. The journey toward sustainability in construction is ongoing and involves continuous learning. Each project presents challenges and opportunities for improvement in our approach to materials tools.
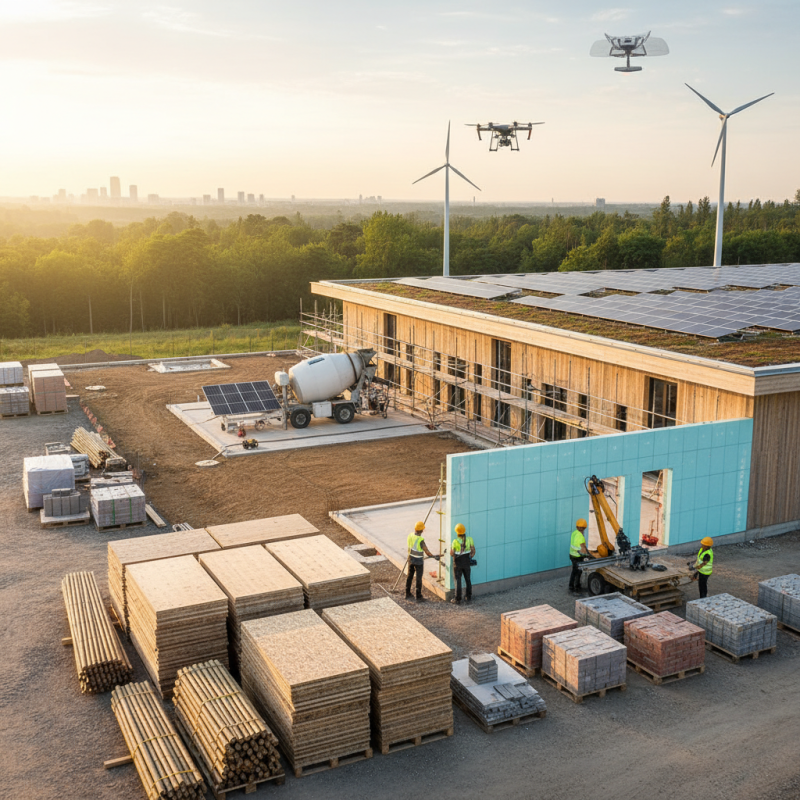

Overview of Sustainable Building Materials
Sustainable building materials play a crucial role in reducing environmental impact. The World Green Building Council highlights that buildings are responsible for about 39% of global carbon emissions. This fact emphasizes the urgency of selecting eco-friendly materials.
Bamboo, for instance, grows rapidly and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. It absorbs carbon dioxide efficiently during its growth, making it a viable option.
Recycled steel is another noteworthy material. According to the Steel Recycling Institute, over 70% of all steel produced in the U.S. is recycled. This reduces the demand for raw materials and decreases energy consumption in production. However, sourcing local materials can sometimes be challenging.
This approach can limit options and impact overall project costs.
Natural insulation materials such as sheep's wool and cellulose are gaining traction. They provide excellent thermal properties and are biodegradable. Yet, availability can vary based on location. The Environmental Protection Agency mentions that many traditional materials still dominate the market, which complicates the transition to sustainable choices.
Creatively overcoming these challenges is essential for the future of green building practices.
Types of Eco-Friendly Construction Materials
Sustainable building projects heavily rely on eco-friendly materials. These materials can significantly reduce environmental impact. One popular option is bamboo, known for its rapid growth and strength. It’s a great alternative to traditional timber and requires less energy to process.
Recycled materials also play a crucial role. Using reclaimed wood or recycled metal cuts waste and energy use. Consider finding local sources to minimize transportation emissions. Recycled glass can create stunning features, adding unique character to a home.
**Tip:** Always assess the lifecycle of materials. Understand how they impact the environment from creation to disposal.
Another interesting choice is straw bales. They provide excellent insulation and are often inexpensive. However, proper treatment is essential to avoid issues with moisture. This choice requires careful planning.
**Tip:** Experiment with combinations. Some materials work better together than alone. Explore the creative potential in building design.
Sustainable construction isn't perfect. It requires ongoing learning and adaptation. Reflect on each choice and its long-term effects. Embrace the journey toward eco-friendliness in your projects.
What is the Best Materials and Tools for Sustainable Building Projects? - Types of Eco-Friendly Construction Materials
| Material Type | Description | Environmental Benefit | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bamboo | A fast-growing, renewable grass that is strong and lightweight. | Carbon sequestration, reduces deforestation. | Flooring, furniture, structural elements. |
| Recycled Steel | Steel produced from scrap metal, reducing landfill waste. | Energy-efficient production, durable. | Structural frames, roofing, reinforcements. |
| Ram Earth | Natural building material made from compacted earth. | Low carbon footprint, enhances thermal mass. | Walls, foundations. |
| Reclaimed Wood | Wood salvaged from old buildings, furniture, etc. | Prevents deforestation and waste. | Flooring, beams, cabinetry. |
| Straw Bales | Bales of straw used as insulation and structural components. | Sustainable waste product, good insulating properties. | Walls, insulation. |
Essential Tools for Sustainable Building Projects
When embarking on sustainable building projects, the right tools are crucial.
Hand tools like hammers, saws, and levels are essential for basic construction. These tools enable precise cuts and accurate measurements.
Compact hand-held power tools also play a vital role. They enhance efficiency and reduce manual effort, making tasks easier.
Measuring tools are fundamental as well. Tape measures provide quick and accurate lengths. Square tools ensure corners are perfectly aligned. Investing in eco-friendly building materials is equally important. They maintain sustainability while enhancing the durability and aesthetics of the structure.
While using tools and materials, it's easy to overlook safety precautions. Sharp tools require care. Inappropriate handling can lead to accidents. Environmental factors also need consideration. Working in adverse weather conditions can affect the integrity of the materials and safety of the project.
Reflecting on these aspects can help improve future projects.
Innovative Techniques in Sustainable Construction

Sustainable construction is rapidly evolving. Innovative techniques are paving the way for eco-friendly practices that minimize environmental impact. One popular technique is using salvaged materials. Reclaimed wood and recycled bricks have unique character and reduce waste. They tell a story and offer charm that new materials lack.
Incorporating natural insulation materials is another great approach. Wool, straw, or hemp can effectively insulate buildings. These materials are not only sustainable but also improve indoor air quality. However, sourcing them can be challenging. Ensure they meet local building codes before use.
Tips: Always research local resources first. Identify nearby suppliers of sustainable materials. Collaborate with local artisans who can provide unique elements. Experiment with different combinations for surprising results. Innovation often stems from trial and error, so embrace imperfections in your process. It’s about progress, not perfection. The journey is just as important as the end product.
Benefits of Sustainable Building Practices
Sustainable building practices offer numerous benefits that can significantly impact both the environment and the economy. According to a 2020 report by the World Green Building Council, green buildings can reduce energy use by up to 50%. This translates to lower utility bills and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, these practices often lead to improved air quality. A study published in the Journal of Sustainable Development found that natural materials and proper ventilation systems contribute to healthier indoor environments.
Tips: Consider using reclaimed wood or recycled materials in your projects. They not only reduce waste but also give unique character to your building.
Another advantage is the potential for increased property value. Properties built with sustainable practices typically see a rise in market demand. People are more aware of climate change and prefer eco-friendly options. However, the upfront costs can deter some builders. It’s essential to weigh initial investments against long-term savings.
Tips: Conduct a life-cycle analysis for your materials. It will help evaluate the long-term impacts and inform better decisions.
Balancing cost and sustainability often requires creativity. Regularly revisiting choices made during planning stages encourages innovative solutions. Adjusting designs based on functionality can enhance sustainability.
Materials and Tools for Sustainable Building Projects
This chart illustrates the percentage of sustainable building materials and tools commonly used in building projects. The data highlights the increasing trend towards using eco-friendly options, showcasing a variety of materials and their corresponding usage in sustainable practices.
Related Posts
-

10 Essential Power Tools Every DIY Enthusiast Should Own for Home Projects
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Drill Tools for Your Projects
-
2025 Top Cutting Tools Trends and Technologies Transforming the Industry
-
Top 2025 Safety Equipment Tools: Essential Gear for Workplace Protection
-

Top Safety Equipment Tools You Need in 2025 for Ultimate Protection
-

Why You Should Upgrade to the Latest Tools for Your DIY Projects

